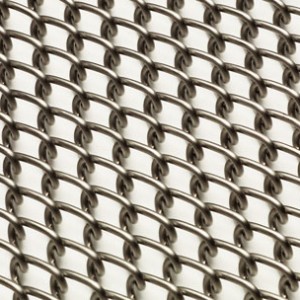
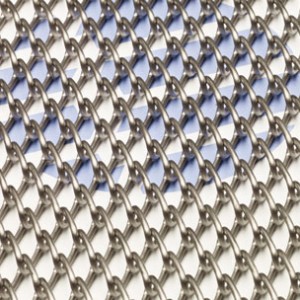
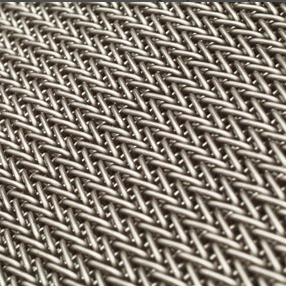
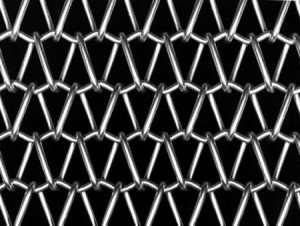
Chain Link features a simplistic design, where successive spiral coils are interwoven to create an open mesh. Chain Link can be supplied with the edges either knuckled or welded.
By keeping the belt design simple yet functional, Wire Belt Company’s Chain Link offers end-users an economic and lightweight solution for low load conveying applications. The large open area inherent in Chain Link’s design also makes it a popular choice for drying and cooling application where belt flow-through is of paramount importance.
Chain Link can be supplied with alternating left and right facing panels to counteract any tracking issues caused by the coil pattern. It is also available as Rod Reinforced Chain Link, where cross-rods are inserted across the belt width to increase the overall load capacity. Chain Link is commonly supplied in Grade 304 Stainless Steel, although other steel grades are available on request.
Standard Chain Link (CL)

The assembly consists of unidirectional coils with each coil interconnecting with the next. When used as a friction driven belt the assembly may feature alternating sections of left then right hand assembled panels. Each belt panel is linked to the next opposite hand weave panel with a through wire – see below. Panelling of the belt with left & right hand coil sections help alleviate belt track off on all circuit rollers and belt supports. Many friction driven belts however are not panelled in this way and rely on their weight and the conveyor tracking system to ensure straight running of the belt.

Rod Reinforced Chain Link (CLR)

To add strength and lateral stability to the belt the intermeshing coils are linked with a through wire. This through wire is finished at the edges in a variety of styles including welded, laddered, knuckled and welded and compressed and welded. When enquiring please forward either a picture or diagram of the belt edge. The same panelling assembly as described above may be required when used solely as a friction driven belt.

Rod Reinforced Chain Link - Duplex (CLR-Duplex)

To add even more belt strength and reduce the open area then a duplex version of the standard rod reinforced is available. The assembly consist of twin intermeshing standard coils at each position.

Standard Chain Link (CL)
These are designed to suit the customer requirements but in general are available in lateral coil wire pitches varying from 5.08mm to 25.4mm, combined with a variety of wire diameters and longitudinal pitches to suit the application.
Rod Reinforced Chain Link (CLR)
|
Lateral Coil Pitch (mm) |
Coil Wire Diameter (mm) |
Longitudinal Cross Wire Pitch (mm) |
Cross Wire Diameter (mm) |
|
16.93/15.24 |
2.03 |
16.93/19.05 |
2.64 |
|
2.64 |
2.95 |
||
|
2.95 |
3.25 |
||
|
3.25 |
4.06 |
Rod Reinforced Chain Link - Duplex (CLR-D)
|
Lateral Coil Pitch (mm) |
Coil Wire Diameter (mm) |
Longitudinal Cross Wire Pitch (mm) |
Cross Wire Diameter (mm) |
|
8.47 |
2.03 |
16.93/19.05 |
2.64 |
|
2.64 |
2.95 |
||
|
2.95 |
3.25 |
||
|
3.25 |
4.06 |
||
|
5.08 |
2.03 |
10.16 |
2.64 |
All dimensions are in millimetres (mm) and are subject to Wire Belt Company manufacturing tolerances.
Edge Availability

Welded Edge (W) – mesh only without reinforcing rods
At the belt edges the coil wires are looped together and welded. This type of edge finish allows for relatively smooth finish to the belt edge and is the most economic version of this belt style.

Knuckled Edge (K) – mesh only without reinforcing rods
The end of each coil wire is bent back into a ‘U’ shape and then interlock with the adjacent coil. The ‘U’ form is then closed securely to form a permanent link with the next coil. This formation also allows greater flexibility of the belt edges and minimises stress build up at these positions.

Edge finish to standard rod reinforced (mesh only) Chain Link Belts
These include the following:
Welded Chain Link Rod Reinforced (CLR-W – IN/OUT). The cross rods are of two different lengths of rod to cater for the edge pattern of coil connection. The cross rods are welded to the coils in an “In – Out” pattern of assembly.

Welded Chain Link Rod Reinforced (CLR-W-IN LINE). All cross rods are the same length with every alternate coil edge compressed to achieve an “In Line” finish.

Chain Link Rod Reinforced Bent Pin with welded edges (CLR-W-BENT-PIN).
With this assembly the cross rods are bent at the ends through 90° and are welded to the preceding coil wire end. To align the edges of the belt, every alternative coil is compressed at the edges prior to welding.
Knuckled Chain Link 'U' Cross Rod Reinforced (CLR-K/U).

With this style of assembly the cross rods are constructed as pairs in a hairclip style 'U' assembly of formation. The 'U' shaped cross rods are kept in place by means of the knuckled coil edges and are inserted alternately from either side when assembling the belt.
As an option to this edge layout the tail end wire of the knuckled coil edges can also be welded back to the coil (CLR-K/U/W).
Edge finish to rod reinforced duplex (mesh only) Chain Link Belts

Welded Duplex Chain Link (CLR-W-Duplex). The assembly consists of pairs of interwoven coil wires with the coil tail ends welded directly to equal length cross wires at the edges.
Knuckled/Hooked Duplex Chain Link (CLR-K/H-Duplex).

Welded Duplex Chain Link (CLR-W-Duplex). The assembly consists of pairs of interwoven coil wires with the coil tail ends welded directly to equal length cross wires at the edges.
Knuckled/Hooked Duplex Chain Link (CLR-K/H-Duplex).
Chain Edge Driven Mesh:
Along with the above mesh edge finishes these meshes can be driven by side chains using cross rods which are located through the mesh coils and then through chains at the edges of the mesh. The types of cross rod finish at the exterior of the side chain are as follows:
With welded washer
This is the most common and economical style of finish to a chain edge belt and comprises of a central mesh carried through the system by means of edge chains with carrier cross rods through both mesh and edge chains. Depending upon the mesh cross wire pitch the cross rods may take the place of the through cross wire of the basic mesh. The cross rods are finished at the outside chain edges with a welded washer

With Cotter Pin & Washer
Although less economical this type of assembly allows the customer or service personnel the ability to replace the edge drive chains when the mesh and rods are still serviceable. The assembly comprises of a central mesh carried through the system by means of edge chains with carrier cross rods through both mesh and edge chains. The cross rods are finished at the outside with a drilled hole to allow the fitment of a washer & cotter pin. It also allows the repair replacement of sections of belt without the need to grind off rod heads and weld back together.
NB: For greater width stability of rods to chain it is normal, where possible, to supply the cross rods turned down to go through the hollow pin of the edge chains.
Various other styles of chain edge finish
These include:
a. Cross rod welded flush to the hollow pin of the side chain. This is not a preferred standard but may be necessary where width between conveyor side frames & other structural parts create a limitation where “welded washer” or “washer & cotter pin” cannot be used.
b. Cross rod welded flush through drilled hole on inner plates of roller conveyor chain.
In general the chain edge driven belts are available with 2 styles of edge chain:-

Transmission Chain - has a small roller
The chain edge side plate can be supported either on an angle side frame, or by means of a profiled rail to go between the side plates and support on the roller. Alternatively it can run without chain support where the mesh is supported close to the chain edge.

Conveyor Roller Chain –has a large roller.
This chain edge can be supported on a flat angle edge wear strip with the chain roller rotating freely along the conveyor length. The roller action of the chain reduces chain wear and also reduces the operational friction at this point.
Methods of Drive
Friction Driven
The most common form of drive is the plain steel parallel driven roller system. This system depends on the frictional contact between the belt and roller to ensure drive of the belt.
Variations of this drive type include the lagging of the roller with such materials as rubber, friction brake lining (for high temperature), etc. The use of such friction lagging materials allow for the operational drive tension in the belt to be reduced, thus increasing the useful life of the belt.


Chain Edge Driven
With this assembly of belt the cross wire pitch of the belt mesh is manufactured to ensure that the chain edge is the driving medium with the belt mesh being pulled through the circuit by the chains.
Standard Material Availability (Mesh Only)
|
Material |
Maximum Wire Operating Temperature °C |
|
Carbon Steel (40/45) |
550 |
|
Galvanised Mild Steel |
400 |
|
Chrome Molybdenum (3% Chrome) |
700 |
|
304 Stainless Steel (1.4301) |
750 |
|
321 Stainless Steel (1.4541) |
750 |
|
316 Stainless Steel (1.4401) |
800 |
|
316L Stainless Steel (1.4404) |
800 |
|
314 Stainless Steel (1.4841) |
1120 (Avoid use at 800-900°C) |
|
37/18 Nickel Chrome (1.4864) |
1120 |
|
80/20 Nickel Chrome (2.4869) |
1150 |
|
Inconel 600 (2.4816) |
1150 |
|
Inconel 601 (2.4851) |
1150 |
Before making a selection for high temperature applications consult with our Technical Sales Engineers for the most suitable wire grade for the application as wire strength reduces at elevated temperatures.